Creating a simple web API using Python and Flask.
In this post we are going to code a small Python/Flask application that connects to a MySQL database to fetch and return a list of people.
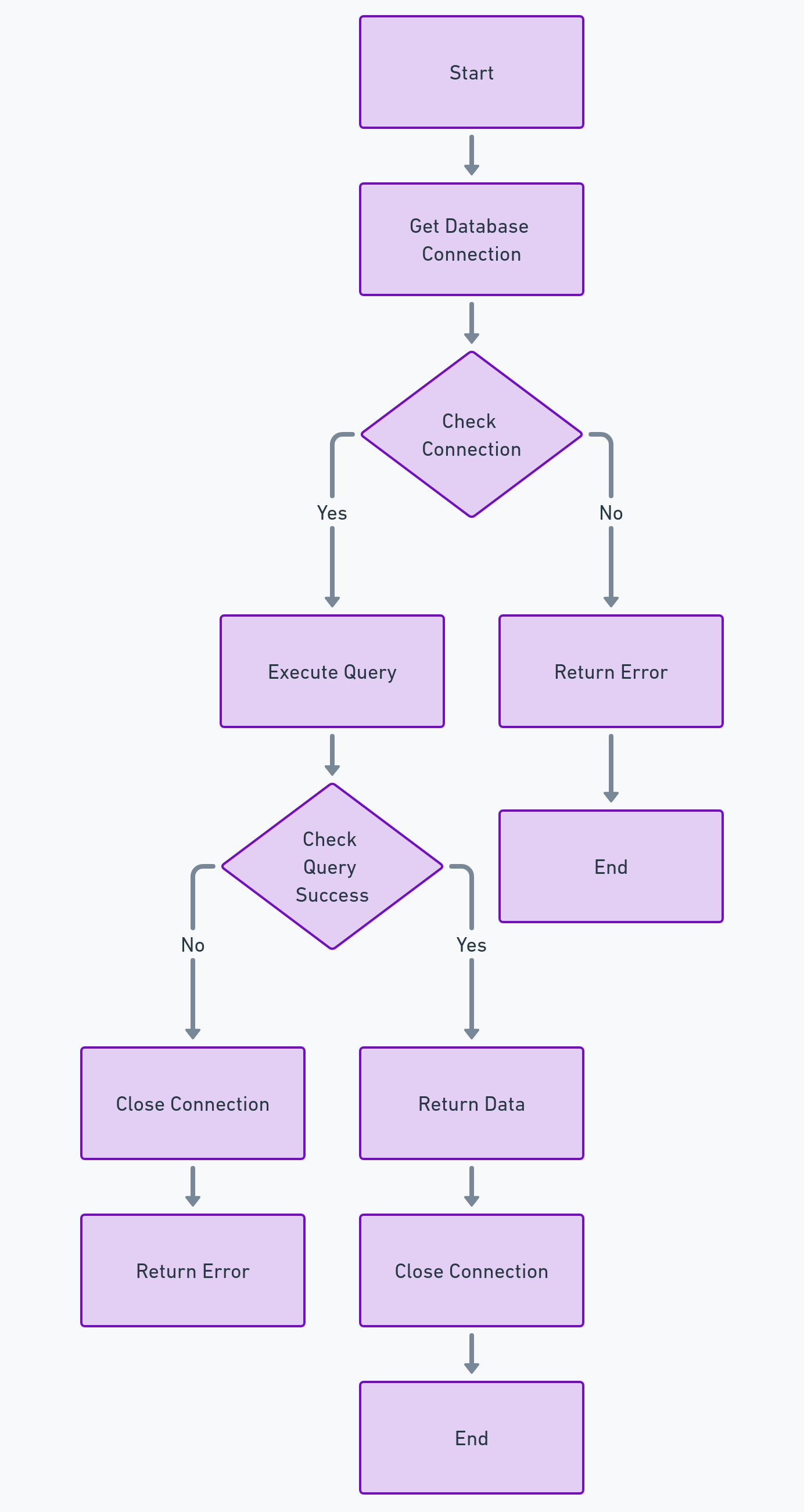
The application is a basic example of a web API developed using Flask. It interacts with a MySQL database to retrieve data and return it in JSON format. This setup is typical for RESTful APIs that serve data to clients, such as frontend applications or other backend services.
1. Imports and Setup:
from flask import Flask, jsonify
import mysql.connector
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
- `Flask` is imported from the `flask` module. It's a class that will be used to create the Flask application instance.
- `jsonify` is a function in Flask used to convert Python dictionaries to JSON responses.
- `mysql.connector` is the Python MySQL driver used to connect to a MySQL database.
- `os` is a standard Python module that provides a way of using operating system dependent functionality.
2. Environment Variables:
db_host = os.getenv('DB_HOST', 'localhost')
db_user = os.getenv('DB_USER', 'root')
db_password = os.getenv('DB_PASSWORD', 'password')
db_database = os.getenv('DB_DATABASE', 'people_db')
- These lines retrieve environment variables which define the database connection parameters (`DB_HOST`, `DB_USER`, `DB_PASSWORD`, `DB_DATABASE`). If an environment variable is not set, it defaults to a pre-defined value (e.g., `localhost` for `DB_HOST`). These values are used to connect to the MySQL database.
3. Database Connection Function:
def get_db_connection():
connection = mysql.connector.connect(
host=db_host,
user=db_user,
password=db_password,
database=db_database
)
return connection - `get_db_connection` is a function that establishes a connection to the MySQL database using the parameters retrieved from environment variables. It uses `mysql.connector.connect()` method to create a connection object and returns it.
4. API Route and Function:
@app.route('/')
def list_people():
conn = get_db_connection()
cursor = conn.cursor(dictionary=True)
cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM people;')
people = cursor.fetchall()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
return jsonify(people)
- `@app.route('/')` is a decorator that tells Flask what URL should trigger the following function, `list_people`.
- Inside `list_people`, a database connection is opened, and a cursor is created with `dictionary=True` to return rows as dictionaries.
- The SQL query `SELECT * FROM people;` is executed to retrieve all records from the `people` table.
- The results are fetched using `cursor.fetchall()`, and both the cursor and connection are closed after retrieving the data.
- Finally, the list of people is returned as a JSON response by wrapping the result in `jsonify()`.
5. Running the App:
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0')
- This is the typical pattern for starting a Flask app. The application will be served on all available network interfaces (`0.0.0.0`) allowing access from other machines on the network.